Today, we will look at how we can implement a Queue by using 2 Stacks in Java. Note that a Queue is an interface in Java and to correctly implement it fully according to the documentation, all of its method signatures must be overridden. In this case however, we are implementing a Queue using our own custom methods and as such, we have omitted the “implements Queue” keyword from the class name. Feel free to add on your own methods as well if you require!
To begin, we will initialise 2 Stacks and name them “s1” and “s2”.
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 |
import java.util.Stack; public class QueueUsing2Stacks<E> { // Initialise stacks Stack<E> s1 = new Stack<E>(); Stack<E> s2 = new Stack<E>(); // Add to queue public void add(E val) { s1.push(val); } // Get size of queue public int size() { return s1.size() + s2.size(); } // Returns true if queue is empty public boolean empty() { if(s1.empty() && s2.empty()) { return true; } return false; } // Returns element at the front of queue public E peek() { if(!empty()) { if(s2.empty()) { while(!s1.empty()) { s2.push(s1.pop()); } } return s2.peek(); } return null; } // Removes and returns element at the front of queue public E remove() { if(!empty()) { if(s2.empty()) { while(!s1.empty()) { s2.push(s1.pop()); } } return s2.pop(); } return null; } } |
Add
Adds an element to the front of the queue. This is done simply by pushing the element onto “s1”.
Size
Returns the number of elements currently in the queue. Adding the number of elements in “s1” and “s2” will give the total number of elements in the queue.
Empty
Returns true if the queue is empty and false if it is not. We know the queue is empty if both “s1” and “s2” are empty as well.
Peek
Returns element at the front of the queue without removing it from the queue. This can be achieved by first checking if the queue is empty and returning a null if it is. Otherwise, we will then proceed to check if there are any elements in “s2”. If there is an element in “s2”, we will simply return that element from the top of “s2” without removing it. If there aren’t any elements in “s2”, we will move all elements from “s1” to “s2” afterwhich we will return that element from the top of “s2” without removing it.
Remove
Removes and returns element at the front of the queue. This can be achieved by first checking if the queue is empty and returning a null if it is. Otherwise, we will then proceed to check if there are any elements in “s2”.If there is an element in “s2”, we will simply remove and return that element from the top of “s2”. If there aren’t any elements in “s2”, we will move all elements from “s1” to “s2” afterwhich we will remove and return that element from the top of “s2”.
How It Works
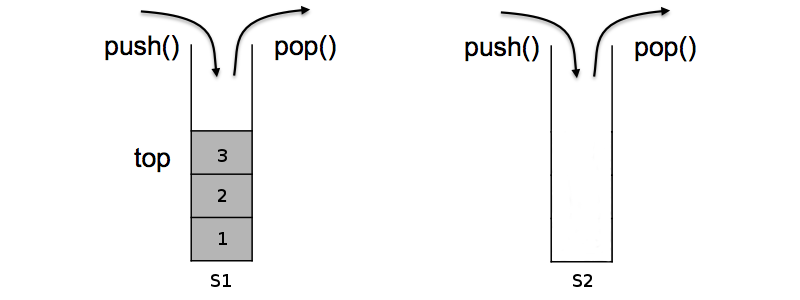
We can see how it works by looking at the following diagram. If we add 3 elements to the queue, they will be pushed onto “s1” as such:
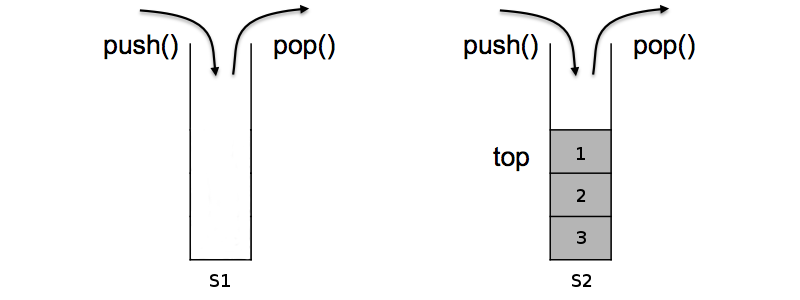
Now, if we wanted to remove elements from the queue, we would first move them over to “s2” since “s2” is empty and then we would pop them out. Notice that the order of the elements has been reversed thus conforming to the First-In-First-Out (FIFO) requirements of a Queue structure.
Try out the code for yourself and see how it goes!
 MooMetric.com Integrating marketing and business metrics using code and non code solutions.
MooMetric.com Integrating marketing and business metrics using code and non code solutions.


Hey There.. I looked at your code and how I am working something related to that. I need help creating a java program that Reverse’s the Sentence. For Example “My Name is Jainam Patel”.. it should Print ” Patel Jainam is Name My”. I Have to Use all the Methods that U Have used in ur code but in two different Classes. One Class is where I ask the user for the Sentence and then use the other methods from other classes to reverse the order. Please Help me Make It.
Thank You.